CAUSES OF DAMAGE TO TURBOCHARGERS
Check why the turbocharger has failed.
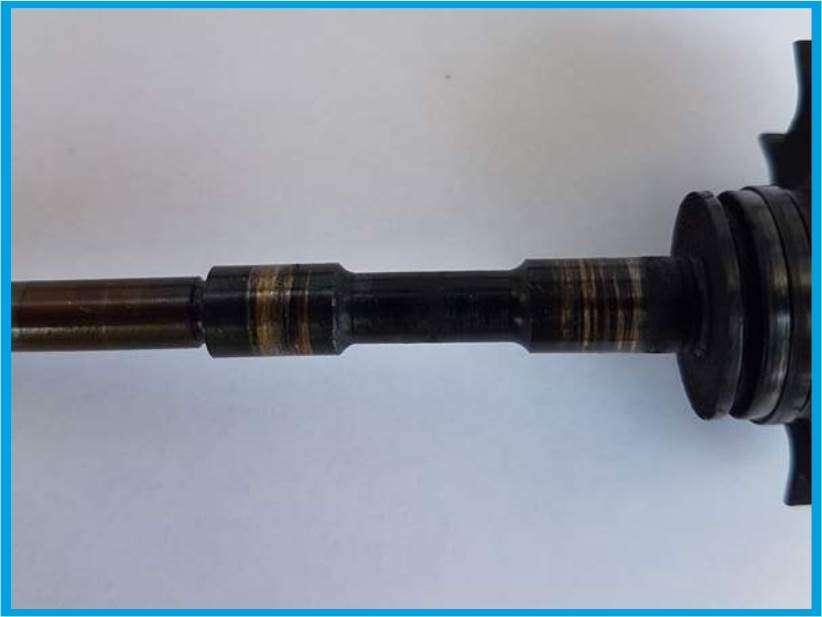
1. CONTAMINATED ENGINE OIL
Irregular replacement or use of low-quality oil can cause the bearings to be operated quickly in the turbocharger. The dirty oil will result in the formation of very deep scratches on the bearings and ultimately the immobilization of the turbine.
Malfunctions related to dirty oil may be caused by:
- Failure to follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding the replacement of oil,
- unchanged oil changes,
- low quality oils,
- damaged, worn or very low quality oil filters,
- engine wear (engines suitable for replacement or major overhaul),
- Insufficient oil filter overflow valve.
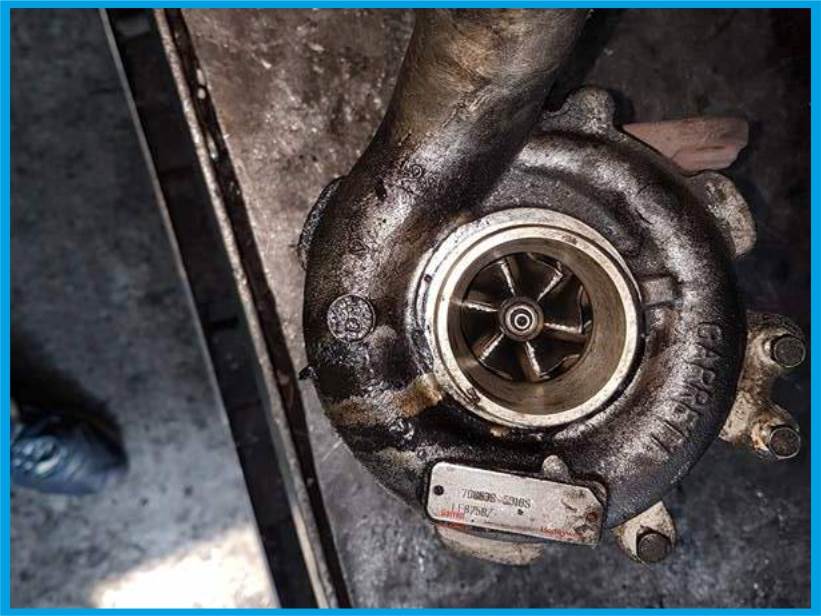


2. DIRTY INTAKE AND EXHAUST SYSTEM
The reason for the pollution of these systems is their improper functioning or improper assembly of the turbocharger. Foreign bodies that have entered the suction body or exhaust turbine cause permanent damage visible to the naked eye on the compression wheel. Sand, splinters of rust or other impurities entering the center of the turbocharger pose a huge threat to rotor blades operating at high speed.
Failures related to a contaminated inlet system may be caused by:
- improper assembly of the turbocharger,
- incorrectly functioning intake system.
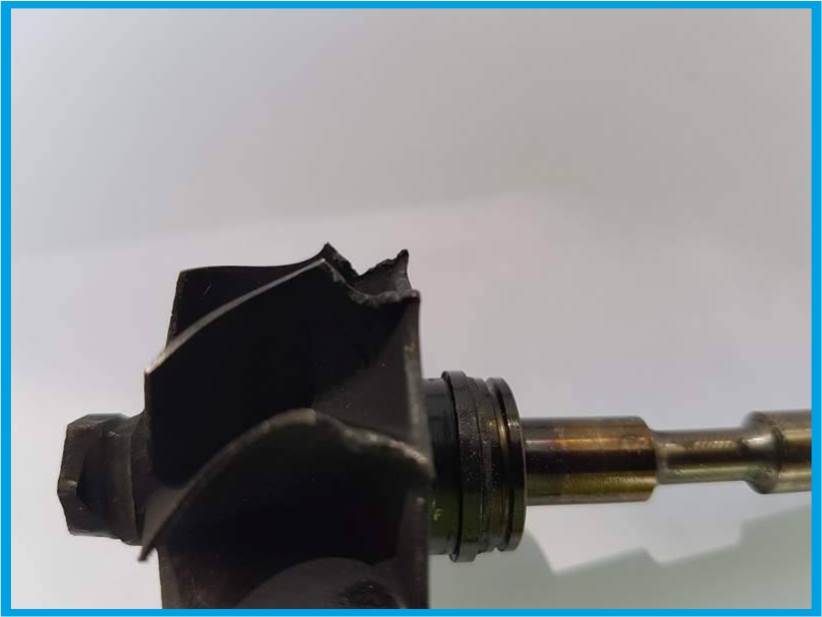
3. BREAKS IN OIL SUPPLY
The oil is essential for the proper functioning of the turbocharger. Gap intervals repeated in 4-6 seconds cycles cause the bearing surfaces to burn out.
Failures related to interruptions in oil supply may be caused by:
- assembly of the turbocharger without prior oil flooding,
- improper oil and oil filter change,
- leaving the vehicle for a long period without burning,
- improper start of the vehicle after replacing the turbocharger,
- bad functioning of the lubrication system,
- increasing the operating temperature by thinning the oil with, for example, fuel.
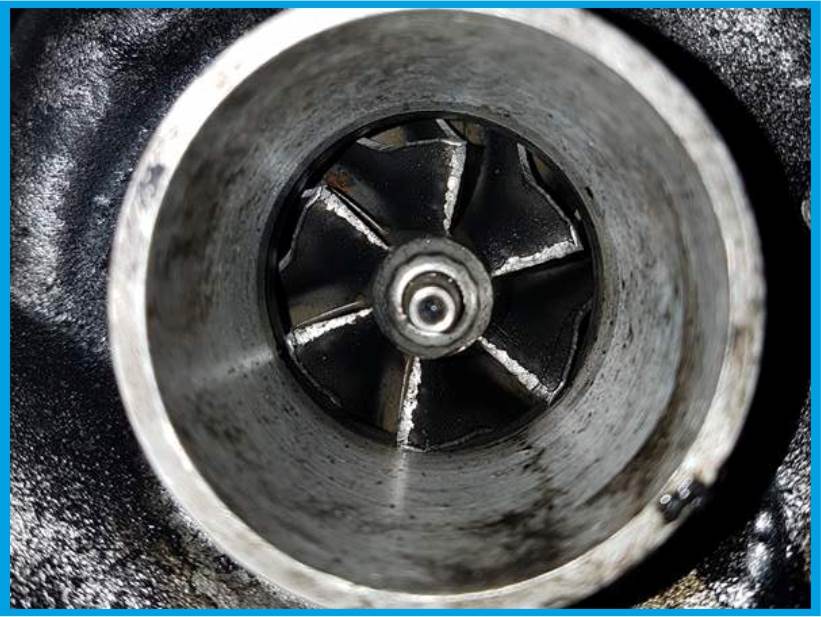
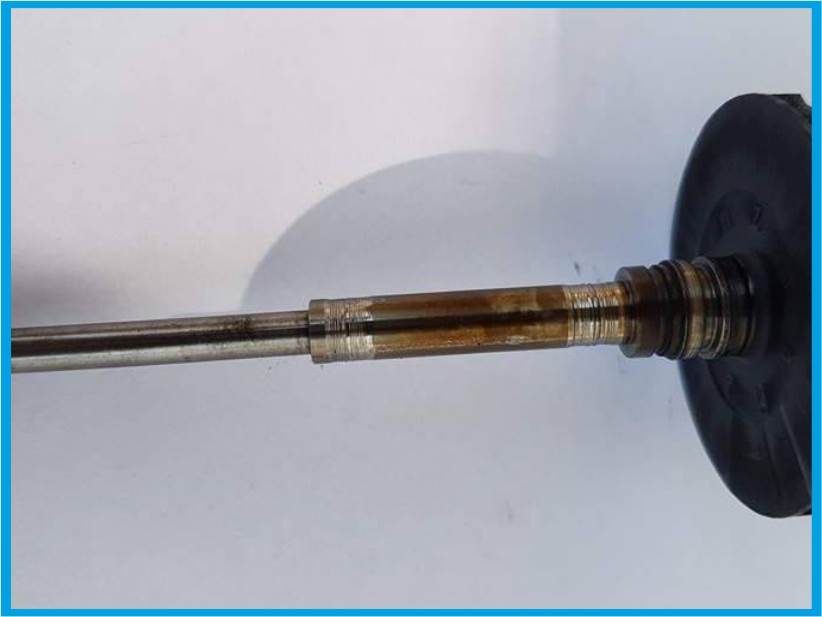


4. IMPROPER OIL PRESSURE
Improper oil pressure is the most dangerous failure and can lead to permanent damage to the turbocharger. Too low pressure will result in failure to deliver the oil turbine, which will result in polishing and burning of bearing surfaces as well as discoloration on the shaft. Regeneration of such a turbine is very difficult or even impossible.
The cause of the wrong pressure can be:
- cracked or obstructed turbocharger lubricating pipe,
- improper operation of the oil pump,
- the oil level in the engine is too low.
5. OVERHEATING
Overheating of the turbocharger qualifies it for replacement with a new one. Regeneration is impossible.
The oil loses lubricating properties and is baked and then charred on the roller, damaging it irretrievably. The reason for charring is too high fumes temperature or turning off the engine after a long drive without cooling the turbocharger. High temperature from the outlet body to the middle causes oil burnout and corrosion of the bearings. The turbine roller rings and grooves are the most vulnerable to failure. The charred oil blocks the outflow of oil in the central body and deposits on the walls causing friction and then cracking of the turbocharger part.
The cause of overheating of the turbocharger may be:
- turning off the engine without cooling the turbocharger,
- blocked air filter,
- Incorrectly fixed turbine body,
- occluded oil drainage system,
- inoperative turbocharger lubrication system,
- air and flue gas purge,
- low quality engine oil,
- damaged injectors,,
- low oil level in the engine.